
How To Fix The RPC Server Is Unavailable Error
- Qcecuring Editorial Team
- 05 Jan, 2026
- 04 Mins read
- Windows Troubleshooting Networking

Introduction
- The RPC Server Is Unavailable error is a common Windows issue that disrupts communication between systems and services.
- It usually appears when Remote Procedure Call (RPC) services fail due to network, firewall, DNS, or service misconfigurations.
- This guide provides a clear, SEO-optimized, step-by-step approach to identify causes and apply reliable fixes, following QCecuring enterprise content standards.
What This Guide Covers
- What the RPC Server Is Unavailable error means
- Common root causes behind the error
- Step-by-step troubleshooting methods
- Network, firewall, and service-level fixes
- Advanced enterprise scenarios and best practices
Workflow Diagram Overview
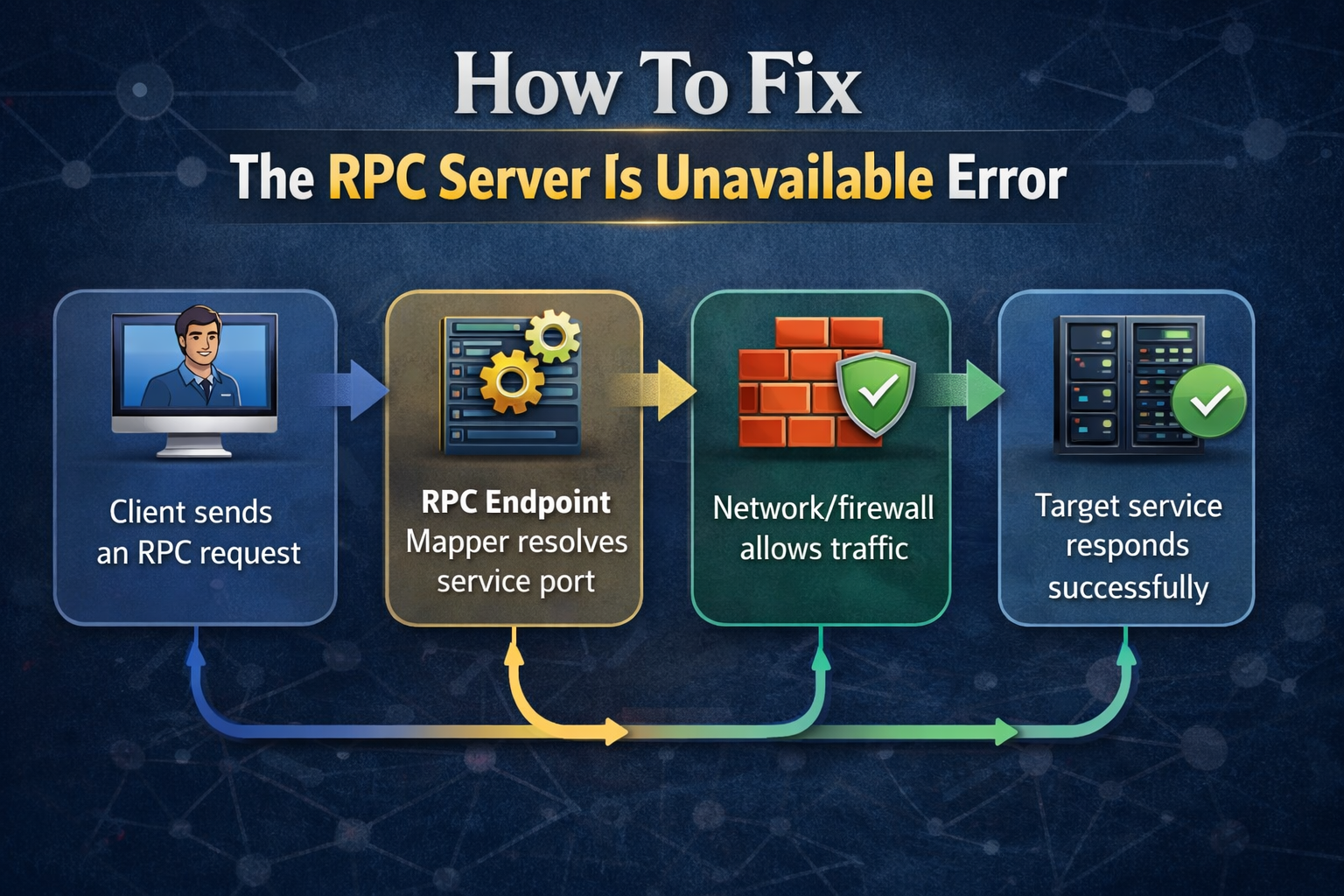
- Client sends an RPC request
- RPC Endpoint Mapper resolves service port
- Network/firewall allows traffic
- Target service responds successfully
1. What Is the RPC Server Is Unavailable Error?
- Indicates failure in Remote Procedure Call communication
- Commonly occurs during:
- Domain joins
- Remote management
- Windows Update
- Printer and file sharing operations
- Impacts:
- System administration tasks
- Enterprise network operations
- Remote service availability
2. Why This Error Matters Today
- Modern Windows environments rely heavily on RPC for:
- Active Directory operations
- Group Policy processing
- Remote PowerShell and WMI
- In enterprise networks, RPC failures can:
- Break automation workflows
- Disrupt Zero Trust and IAM operations
- Cause compliance and availability risks
3. Common Causes of the RPC Server Is Unavailable Error
- RPC-related services not running
- Firewall blocking required ports
- DNS or name resolution failures
- Network connectivity issues
- Corrupted system files
- Incorrect registry configurations
4. Step-by-Step Fixes (Technical Deep Dive)
4.1 Verify RPC Services
- Ensure the following services are Running and Automatic:
- Remote Procedure Call (RPC)
- RPC Endpoint Mapper
- DCOM Server Process Launcher
Get-Service RpcSs,DcomLaunch,RpcEptMapper4.2 Check Network Connectivity
- Ping the target system
- Verify IP address and subnet alignment
- Test name resolution
ping hostname
nslookup hostname4.3 Configure Firewall Rules
- Ensure these ports are allowed:
- TCP 135 (RPC Endpoint Mapper)
- Dynamic RPC ports (TCP 49152–65535)
4.4 Validate DNS Configuration
- Confirm correct DNS servers are configured
- Flush and renew DNS cache
ipconfig /flushdns
ipconfig /renew4.5 Check System File Integrity
- Scan and repair corrupted system files
sfc /scannow5. Architecture Workflow
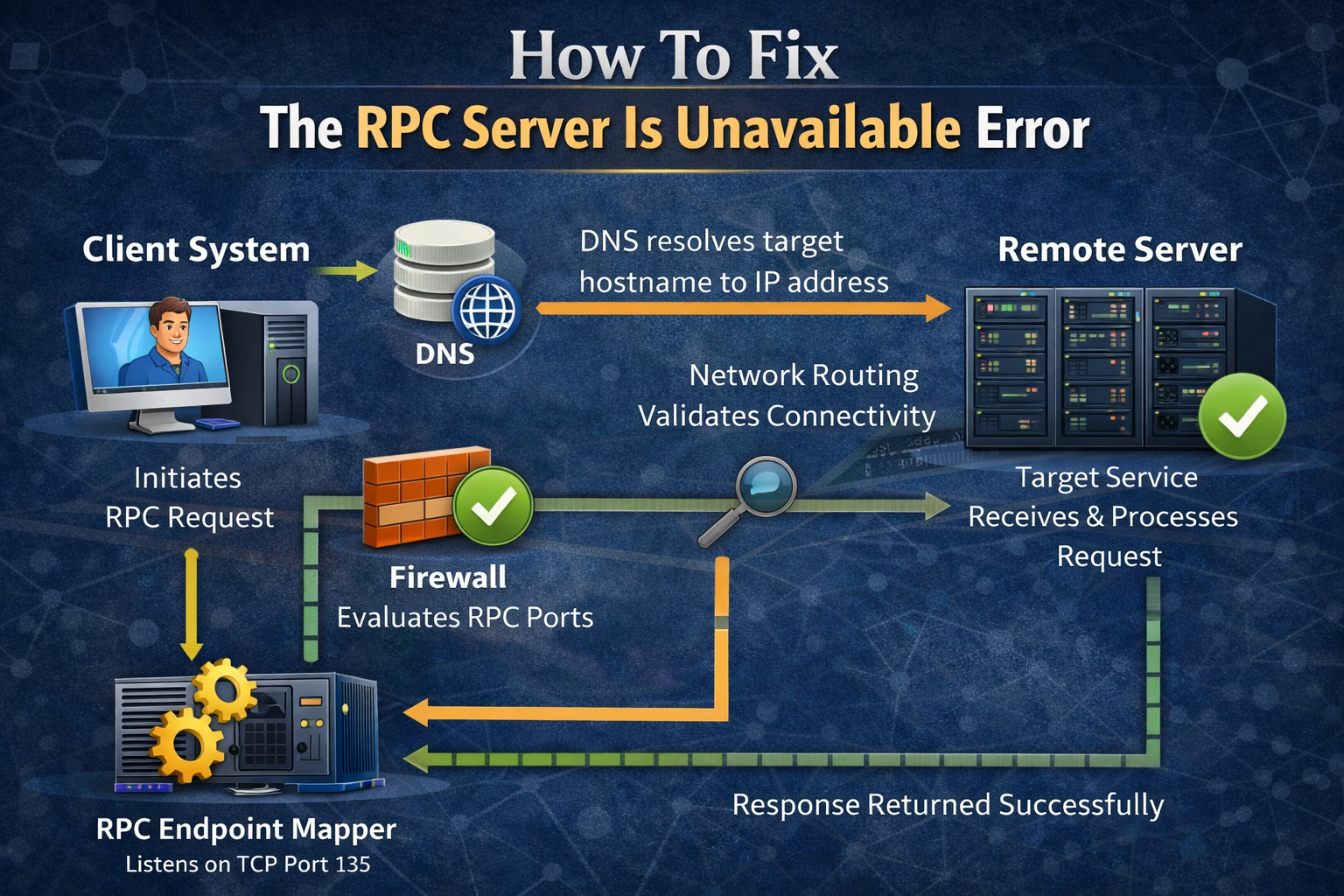
- Client system initiates an RPC request to a remote server
- DNS resolves the target hostname to an IP address
- Network routing validates connectivity between client and server
- Firewall evaluates and allows RPC-related ports
- RPC Endpoint Mapper listens on TCP port 135
- Dynamic RPC port is assigned for the requested service
- Target service receives and processes the request
- Response is returned to the client successfully
6. Best Practices to Prevent RPC Errors
- Keep Windows operating systems fully patched and updated
- Ensure RPC-related services are always enabled and monitored
- Maintain consistent firewall rules across all environments
- Allow required RPC static and dynamic port ranges
- Use centralized DNS servers and avoid split-brain DNS issues
- Monitor Event Viewer logs for early warning signs
- Validate network changes in staging before production rollout
- Document RPC dependencies for critical applications
- Implement controlled network segmentation with testing
- Regularly audit service and port configurations
7. Common Pitfalls
- Disabling RPC or DCOM services for security hardening
- Blocking dynamic RPC ports unintentionally at the firewall
- Misconfigured DNS servers or incorrect name resolution
- Overlooking VPN or remote network policies
- Applying registry changes without proper backups
- Ignoring system and security logs during troubleshooting
8. Advanced Enterprise Scenarios
- RPC failures impacting Active Directory replication
- Issues in hybrid cloud and on-premises integrations
- Remote management failures using WMI or PowerShell
- RPC disruptions caused by Zero Trust microsegmentation
- Challenges in multi-domain or multi-forest environments
- VPN-connected endpoints experiencing intermittent RPC errors
Competitor Comparison
| Capability | QCecuring | DigiCert | Venafi | Keyfactor | Encryption Consulting |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Automation-First Architecture | Yes | Limited | Partial | Partial | No |
| RPC & Windows Infrastructure Expertise | Advanced | Basic | Moderate | Moderate | Basic |
| Enterprise Troubleshooting Depth | High | Medium | High | High | Medium |
| Cloud & Hybrid Environment Support | Native | Partial | Advanced | Advanced | Limited |
| Zero Trust Alignment | Built-in | Limited | Advanced | Advanced | No |
| Policy-Driven Remediation | Advanced | Basic | Advanced | Advanced | Basic |
| CI/CD & Infrastructure Automation | Native | Partial | Partial | Partial | No |
| Scalability for Large Enterprises | High | High | High | High | Medium |
| Compliance & Audit Readiness | Strong | Strong | Strong | Strong | Moderate |
QCecuring differentiates itself with automation-first, enterprise-grade troubleshooting and remediation capabilities designed for modern, hybrid, and Zero Trust Windows environments.
Keyword Expansion Zone
- fix RPC server unavailable error
- RPC server unavailable Windows 10
- RPC server unavailable Windows 11
- Remote Procedure Call error troubleshooting
- RPC firewall port configuration
- Windows RPC connectivity issue
External Resources
- Microsoft Remote Procedure Call documentation
- Windows Firewall and RPC port configuration guidance
- Enterprise Windows networking best practices
Final Summary
- RPC errors usually stem from service, network, or firewall issues
- Verifying services and connectivity should be the first step
- Firewall and DNS misconfigurations are common root causes
- Enterprise environments require standardized configurations
- Proactive monitoring helps prevent recurring RPC failures
FAQs
Q1. What does RPC Server Is Unavailable mean?
- It indicates a failure in communication between systems using RPC.
Q2. Is this a network or Windows issue?
- It can be caused by network, firewall, DNS, or Windows service problems.
Q3. Which ports are required for RPC?
- TCP port 135 and a range of dynamic high ports are required.
Q4. Can antivirus software cause this error?
- Yes, security software may block RPC traffic or services.
Q5. Does this error affect Active Directory?
- Yes, RPC is critical for Active Directory operations.
Q6. Is restarting the RPC service recommended?
- No, restarting core RPC services is not recommended on production systems.
Ready to Secure Your Enterprise?
Discover how QCecuring can help you automate certificate lifecycle management, secure SSH keys, and protect your cryptographic infrastructure.
