- QCecuring Team
- 13 Oct, 2025
- 03 Mins read
- Security Encryption
A Certificate Signing Request (CSR) is a message generated by an applicant for a digital certificate. It contains essential information about the applicant and their public key and is sent to a Certificate Authority (CA) to request the issuance of a digital certificate. Proper CSR generation and management are critical for securing enterprise communications.
What is a CSR?
A CSR includes the following key information:
- Applicant’s name and contact information
- Applicant’s public key
- Domain name or system for which the certificate is requested
The CA uses the CSR to verify the identity of the applicant and issue a digital certificate that is signed with the CA’s private key. The issued certificate then allows for authentication and encrypted communication.
How Does a CSR Work?
Step 1: Key Pair Generation
The applicant generates a public-private key pair using a cryptographic algorithm such as RSA, ECDSA, or EdDSA.
- Private Key: Kept secret for signing and decryption.
- Public Key: Included in the CSR and used for verification and encryption.
Step 2: CSR Creation
Using a server tool or command-line utility, the applicant generates the CSR:
# Example using OpenSSL
openssl req -new -newkey rsa:2048 -nodes -keyout mydomain.key -out mydomain.csr
This creates:
mydomain.key → Private key
mydomain.csr → Certificate Signing Request
Step 3: Submission to CA
The CSR is submitted to a CA, optionally along with identity proofs or payment. The CA validates the CSR details and issues a signed certificate.
CSR Generation Output
When a CSR is generated, it typically produces two files:
mydomain.key→ Private Key (keep this secure and confidential)mydomain.csr→ Certificate Signing Request (to be submitted to a CA)
Step 3: Submission to Certificate Authority (CA)
The CSR is submitted to a Certificate Authority (CA), optionally along with identity proofs or payment. The CA will:
- Validate the CSR details.
- Verify the applicant’s identity.
- Issue a signed digital certificate.
This certificate can then be used for secure communications, authentication, and encryption.
Why is a CSR Important?
A CSR plays a critical role in securing digital communications:
- Authentication: Verifies the identity of the certificate requester.
- Encryption: Enables secure communication over HTTPS, VPNs, and internal systems.
- Compliance: Ensures enterprise systems follow security and regulatory standards (PCI DSS, ISO 27001, NIST).
Without proper CSR generation, online communications are vulnerable to interception and attacks.
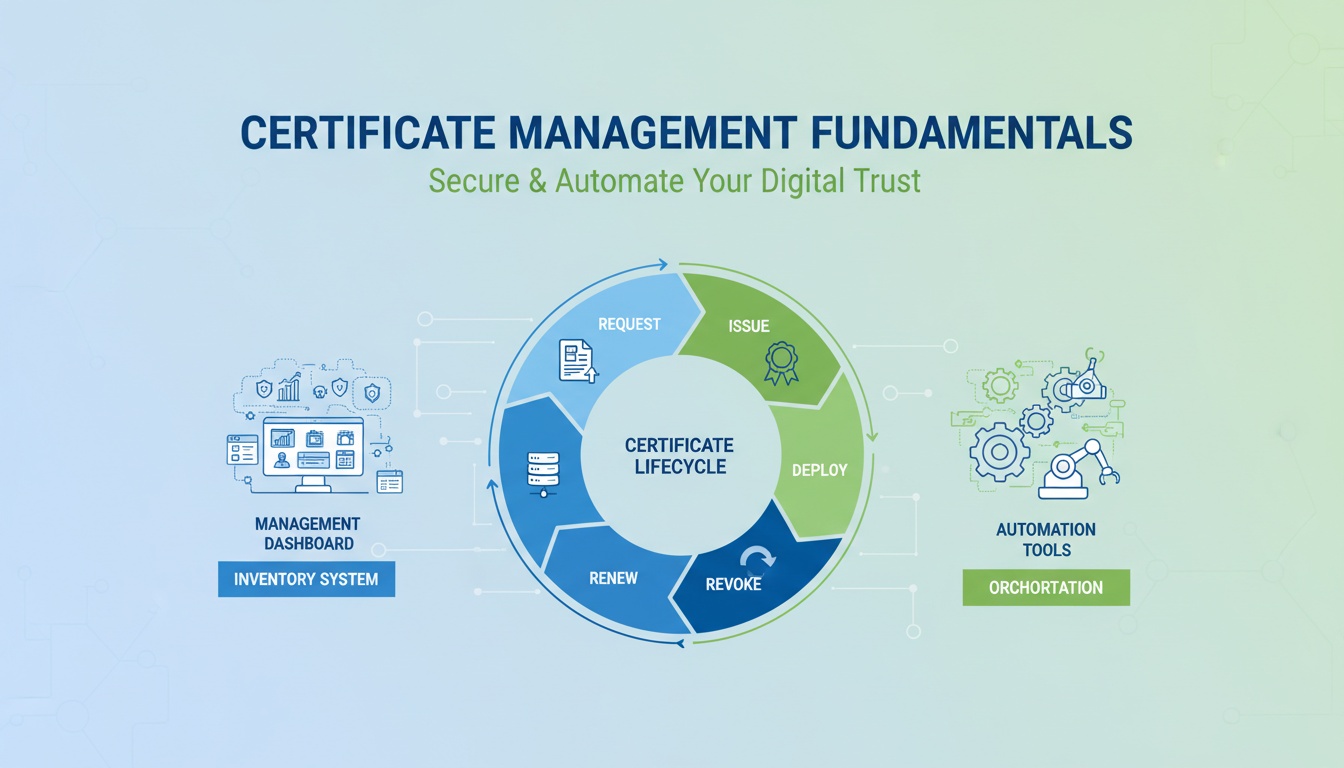
What is Certificate Lifecycle Management (CLM)?
Certificate Lifecycle Management (CLM) is the end-to-end management of digital certificates from creation to revocation.
Key processes include:
- Certificate Issuance: Automates CSR generation and submission.
- Renewal: Ensures certificates do not expire unexpectedly.
- Revocation: Quickly revokes certificates in case of compromise.
- Replacement: Updates certificates with minimal downtime.
How CLM Helps in CSR Generation
CLM ensures secure and standardized CSR generation across the enterprise:
- Standardization: All CSRs follow corporate policies and include required attributes.
- Applicant Verification: Automates identity checks to prevent fraudulent requests.
- Secure Private Key Management: Private keys are generated, encrypted, and stored securely.
- Audit & Compliance: Tracks CSR creation and certificate issuance for regulatory reporting.
- Integration with DevOps & PKI: Supports automated CSR generation in CI/CD pipelines, microservices, and cloud environments.
Latest Enterprise Practices in CSR & CLM
- Cloud Integration: Central management of CSRs and certificates for hybrid environments (AWS, Azure, GCP).
- Automated Renewal: Reduces risk of expired certificates causing service downtime.
- Advanced Key Algorithms: Use of ECC (Elliptic Curve Cryptography) for stronger security with smaller key sizes.
- Zero-Touch Deployment: Automatic distribution to servers, endpoints, and applications.
- Post-Quantum Preparedness: Exploring quantum-resistant algorithms for future-proof security.
Best Practices for CSR Generation in Enterprises
- Use trusted cryptographic libraries for key and CSR generation.
- Always use strong key sizes (e.g., RSA 2048+ or ECC P-256+).
- Ensure CSR attributes comply with internal security policies.
- Encrypt and protect private keys during storage and transmission.
- Audit CSR generation and certificate issuance for regulatory compliance.
Example: CSR Fields
Common Name (CN): www.example.com
Organization (O): Example Corp
Organizational Unit (OU): IT Security
City / Locality (L): New York
State / Province (S): NY
Country (C): US
Email: admin@example.com
Public Key Algorithm: ECC P-256Ready to Secure Your Enterprise?
Discover how QCecuring can help you automate certificate lifecycle management, secure SSH keys, and protect your cryptographic infrastructure.